what constitutes failure for wood under compressive testing|Compression failure mechanism in small scale timber specimens : importer Compressed wood (CW) Wood can be compressed in two of the three main directions (i.e. radial and tangential directions). In contrast, compression of wood in the longitudinal direction .
Resultado da Google Académico ofrece una forma sencilla de buscar literatura académica. Puedes buscar entre una amplia gama de disciplinas y fuentes académicas, como artículos, tesis, libros, resúmenes y dictámenes jurídicos.
{plog:ftitle_list}
3 dias atrás · Welcome to Atlanta – vibrant, cultural hub of the Southeastern USA. While Atlanta is a popular, bustling city with glittering skylines, it is also a city in the forest, dotted with expansive green spaces and charming neighborhoods. Discover hidden gems around every corner, including diverse dining, top attractions, incredible arts and .
The established finite element model could effectively simulate the compressive failure process of wood with initial defects, validating the effectiveness of numerical .Methods of Detecting Compression Failures in Wood or Wood Parts Compression failures are easier to detect on smoothly sawn or planed surfaces or in finished lumber, than in rough .
Purpose: During this laboratory you will learn about: Measurement techniques for compression testing. Mechanical properties of Wood. Effects of directional properties on strength and .Several wood species, hardwoods and softwoods, are tested under compression parallel to grain to investigate experimentally the formation of kink bands and the relationship between this.Off-axis compression tests (OACT) were conducted on solid wood from six tree species, and the relationship between the off-axis compressive strength (OACStr) and the off-axis angle was .Compressed wood (CW) Wood can be compressed in two of the three main directions (i.e. radial and tangential directions). In contrast, compression of wood in the longitudinal direction .
Understanding the failure mechanism of wood loaded in compression parallel to the grain has been shown to be an important parameter in the design of timber beams .
Failure types of nonbuckling clear wood in compression parallel to grain: (a) crushing, (b) wedge splitting, (c) shearing, (d) splitting, (e) crushing and splitting, (f) brooming or end rolling. This investigation focuses on the experimental developments of the geometry and test set-up necessary in order to determine the compression failure mechanism of small .
This study aimed to discuss the influence of specimen sizes on the compressive strength parameters of wood, specifically focusing on their compression strength, elastic modulus, and Poisson’s ratio. Therefore, three .
The motivations to detect and identify compression wood are manifold and so are the demands on a proper solution of this problem. At present, biological detection and classification offer the most detailed grading of compression wood against normal wood, while visual inspection enables fast detection of compression wood in its spatial orientation on .
Off-axis compression tests (OACT) were conducted on solid wood from six tree species, and the relationship between the off-axis compressive strength (OACStr) and the off-axis angle was predicted under the conventional Hill-type quadratic failure conditions, off-axis special failure conditions, and under a condition proposed in this study, which contains terms of interaction . The mechanical properties of wood vary in different grain orientations due to its anisotropy nature (Takuro 2005; Piotr et al. 2021).In practice, finding timber with an ideal radial, tangential or longitudinal grain orientation is challenging, and large amounts of timber under compressive load at the structural joints usually have a cross-grain orientation (Nairn 2007).
It is important to remember that solid wood only constitutes 5% of this balsa specimen. Consequently, the failure zone does not broaden very much as crushed material is added to it. . The testing machine was operated under displacement control using a close-loop controller. For more accurate measurements, a miniature LVDT was used to measure . Standard Used. ASTM D 1037. Objective. Following are the objectives of performing this experiment: To determine the compressive strength of wooden cubes parallel and perpendicular to the grains; To investigate the stress-strain relationship in wooden cubes to determine the modulus of elasticity and modulus of stiffness; To discern the anisotropic .
The established finite element model could effectively simulate the compressive failure process of wood with initial defects, validating the effectiveness of numerical simulation. Bažant's size effect theory can be used for size effect analysis of the compressive strength of wood with initial defects in the longitudinal direction. Off-axis compression tests (OACT) were conducted on solid wood from six tree species, and the relationship between the off-axis compressive strength (OACStr) and the off-axis angle was predicted .
• Describe what constitutes failure for wood under compressive testing. What is the nature of the failure? • Mention briefly what differences can be seen between the properties of the hard and soft woods. Table 3: Failure Loads Wood Name. Test Type Specimen No. 1 -, :. Failure Load (kN) -. The failure process in wood under compression failure, with the formation of kinkbands, is fairly well understood and several experimental studies have been reported . parallel to the fibres. To do this, the development of an experimental method was carried out, based on existing compression testing methods used for unreinforced wood . Compression testing of composites can be a minefield. With many fixture variations & a seemingly endless multitude of standards. . When buckling failure occurs, the only thing that has been determined is that the compressive strength of the material is higher than the stress at which buckling has occurred. . Modelling failure of composite .
Compression of wood and wood-based materials plays an important role in almost any construction projects. If the compression strength or bending strength of a 2-inch by 4-inch beam is not known, deflection due to bearing a load may cause significant deformation, which could even lead to its failure during service life.
issue, this paper presents a comprehensive test programme and an extensive database of CW materials. It in-cludes experimental results of over 720 material tests that were conducted on CW materials. The fundamental tests under compression, tension, bending, embedment, yield moment, shear and impact tests were undertaken.Illustrative of compression failures formed in the living tree, apparently as the result of a storm many years prior to felling, is the piece of a Sitka spruce board shown in figure 1.Formation of the compression failure shown in the figure, evidently injured the .
Test methods. The compression tests of the specimens with the loaded cross-section of 30 × 30 mm 2 were carried out on an Instron testing machine with an in-line 100-kN load cell under displacement controlled .Measuring the compressive strength of a steel drum. In mechanics, compressive strength (or compression strength) is the capacity of a material or structure to withstand loads tending to reduce size (compression).It is .
In this study a review of existing recognised standards for wood mechanical testing was conducted. This review considers tensile, compressive, bending and shear test methodologies from a range of .Failure types of clear wood in tension perpendicular to grain: (a) tension failure of earlywood, (b) shearing along a growth ring, (c) tension failure of wood rays. Flexure Failure types of clear wood in bending with span parallel to grain: (a) simple tension, (b) cross-grain tension, (c) splintering tension, (d) brash tension, (e) compression . The failure of concrete under compressive loads is determined to be due to local buckling [4], . Even so, there is no definite concept or a complete basis for what fully constitutes the difference of strength for various specimen geometries, it is very complex and very difficult to completely factor out all the parameters. . For compression .
The design of wood structures, such as columns and beams, requires the knowledge of the compressive behavior of wood. Several wood species, hardwoods and softwoods, are tested under compression .Oak Compression Perpendicular to Grain. Oak 2. Compression Parallel to Grain. Pine 1. Pine Compression Perpendicular to Grain. Pine 2. Thickness refers to the width of the block. Describe what constitutes failure for wood under compressive testing. What is . Compressive testing is a type of mechanical testing that measures the compressive strength of a material. The compressive strength is the maximum stress a material can endure before breaking under compression. This type of testing is used to determine essential properties such as: Modulus of elasticity; Proportional limit; Compressive yield point
Compression Test: Compression testing loads a standardized test block axially, with pure compressive force, which tends to shorten the sample in the compressive axis and bulge the sides, making a complex load scenario. The material's ability to resist compression is a critical piece of design knowledge and provides compressive strength and . Testing is the only way to determine whether a concrete mix has enough compressive strength, or load-bearing capacity, for the intended use. These tests are conducted on cylindrical concrete specimens (per ASTM C39 ) using a machine that compresses the cylinders until they crack or break completely (see Concrete Testing Procedures ). Compressive strength is a fundamental parameter that informs the safety, quality and durability of a particular mix of concrete. Testing according to ASTM C39 is central to the QA/QC process. For over 80 years, ASTM C39 has been the industry standard test method for testing the compressive strength of concrete cylinder specimens. In this .Following are the procedure for testing the Compressive strength of Concrete Cubes Apparatus for Concrete Cube Test. Compression testing machine. Preparation of Concrete Cube Specimen. The proportion and material for making these test specimens are from the same concrete used in the field. Specimen. 6 cubes of 15 cm size Mix. M15 or above
Furthermore, this test determines the load which the wood can support over a period. Relevant IS codes: IS I 2380 ( Part VI ) – 1977 . Initially, take a specimen with a size of 5cm x 5cm x 20cm. Then place the specimen in the compressive testing machine. Following this, apply load parallel to the grains. The specimen should be free from .
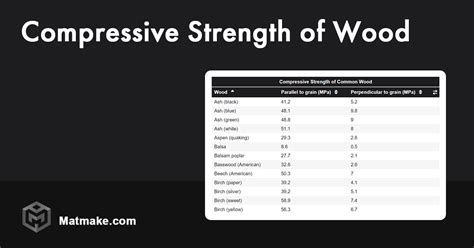
The Strength of Wood
Possible modes of deformation in compression
First, make sure you understand the question, ask clarifying questions of your own if needed. Decide if you want to answer the question: you have the option to divert, delay or return. If you do answer, use this simple structure: Answer the question with a quick, simple, direct answer. Add additional ‘bullets’ if needed.
what constitutes failure for wood under compressive testing|Compression failure mechanism in small scale timber specimens